While much of the focus of autonomy has been on cars and trucks, trains could also benefit from the technology. Cognitive Pilot today said it has has received a Declaration of Conformity with technical regulations of the Eurasian Economic Union for its Cognitive Rail Pilot locomotive driver-assistance system. The document certifies that the system is safe for both consumers and the environment and that it meets technical safety requirements for “railway rolling stock.”
“This declaration of conformity with the requirements of the Eurasian Economic Union technical regulations is the result of comprehensive tests of Cognitive Rail Pilot system that took place in 2021,” stated Olga Uskova, CEO of Cognitive Pilot. “[It] is an important step for the system's further development and scaling.”
“This is another confirmation of the system's high level of quality and safety, which gives us an additional opportunity for the mass production of Cognitive Rail Pilot on an industrial scale for several countries at once,” she added. “Our programmers, neural network specialists, and engineers have done a tremendous job.”
Cognitive Pilot an autonomous driving joint venture of Sberbank and Cognitive Technologies Group. The Moscow-based company has developed machine vision and artificial intelligence for autonomous equipment for agriculture, rail transport, and urban transportation.

Robots on the rails for safety
Ensuring safe operations is a key challenge for the global railway transport industry, noted Cognitive Pilot. Accidents involving people or vehicles on railway tracks occur almost every 2 hours, according to the U.S. National Transportation Safety Board. Analysts and industry experts said human error is a significant cause of railway accidents, which cost hundreds lives in the U.S. annually and billions of dollars to repair the infrastructure.
“Experts around the world are unanimous in saying that robotization of railway operations can solve the problem of traffic safety,” said Uskova. “The locomotive driver profession is one of the most difficult and dangerous—you have to work to the limit. Robots can take away the driver's routine workload and provide assistance in emergency situations.”
“When our Cognitive Rail Pilot goes into mass production, we are confident that the level of safety in railway maneuvering operations will rise to a whole new level, with incidents falling by up to 70%,” she said. “The economic model of using the system provides a quick return of investment by improving the rhythm of locomotive operations.”
The global market for autonomous railway transport control systems is growing rapidly. It is valued at more $7 billion today, and it could exceed $21 billion in volume by 2031, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.4%, predicted Visiongain.
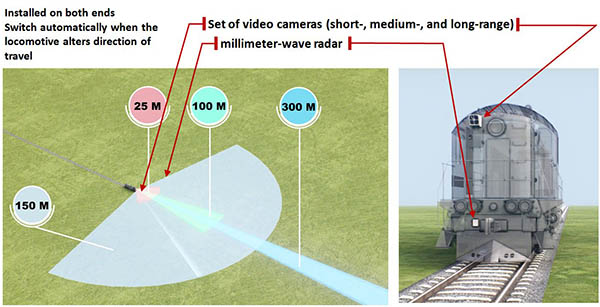
Cognitive Rail Pilot focuses on perception
“Cognitive Rail Pilot is an AI-based system that allows the locomotive to 'see' and 'understand' the situation along the way with high accuracy,” said Cognitive Pilot. The technology, which is similar to advanced driver-assist systems (ADAS) for cars, can warn a driver of danger, and in the case of a lack of response, automatically perform a safe stop.
In addition, the company said its system can determine the location and dynamics of the locomotive with a very high degree of accuracy. Cognitive Pilot said it has developed computer vision technology based on deep learning neural networks, millimeter radar technology, and special algorithms for post-processing data to meet accuracy and reliability requirements.
The modules of the Cognitive Rail Pilot system include the following components:

A multi-zone camera unit including:
- Close-up, mid-range and long-range cameras
- Protective cover with wiper
- Interior heating system
- Vibration damping and active vibration-damping system
- Independent control and monitoring controller
CPRR24 millimeter-band radar:

- Operating frequency 24 GHz
- Working range 250 m (820.2 ft.)
- Viewing angle 120°
- Accuracy of target distance < 0.15 m (0.4 ft.)
- Accuracy of target azimuth <1°
- Accuracy of target velocity <0.1 km/h (0.06 mph)
- Operates independently of rainfall
Computing module:

- 65 TFLOPS (trillions of operations per second) performance
- Power Protection Suite
- Independent controller for monitoring the health of the calculator
- Complex sensor connection interfaces
- Interfaces to the locomotive's onboard systems
- Onboard data-transfer modem
The system's main functions include stopping at a red light, stopping in danger of a collision, stopping before a closed arrow, and verifying the location of a locomotive with high precision, said Cognitive Pilot.
Labs rigorously test railway system
The Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) regulation applies to recently developed railway rolling stock and its parts destined for the use on the railroads in the region, explained Cognitive Pilot. The “railway rolling stock” includes locomotives, motorized cars and trains, special railway rolling stock, and freight cars.
To obtain approval for mass production and confirm its compliance with established industry standards for railway rolling stock traffic safety and information security, specialized laboratories tested Cognitive Rail Pilot. They were accredited by Russian Railways.
The labs examined the source code for Cognitive Rail Pilot, said Cognitive Pilot. They also tested its hardware on dozens of parameters, such as electromagnetic compatibility, noise resistance, vibration resistance, compliance with climatic norms, and resistance to moisture.
Cognitive Rail Pilot needed to achieve a high level of accuracy in detecting dangerous objects and situations, noted the company. The system is able to ensure the safe operations in rain, snowfall, fog or night.
In addition, Cognitive Rail Pilot must be able to work in temperatures ranging from -40°C to +50°C (-40°F to 122°F), where the Russian Railways rolling stock operates.
Last year, Cognitive Rail Pilot underwent a set of running tests on rolling stock. Smart locomotives with a driver-assist system ran for more than 300 hours in tests with the company's specialists. It ran for over 5,000 hours of supervised operation without their presence, proving that all technical characteristics correspond to those stated in the TOR.
The EAEU certification allows Cognitive Pilot to start sales and deliveries of the Cognitive Rail Pilot system to Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan.
Article topics
Email Sign Up

















