Robots are increasing in complexity, with a higher degree of autonomy, a higher number and diversity of sensors, and more sensor fusion-based algorithms. Hardware acceleration is essential to run these increasingly complex workloads, enabling robotics applications that can run greater workloads with more speed and power efficiency, according to NVIDIA.
The mission of NVIDIA Isaac ROS has always been to empower ROS developers with the accelerated computing packages and tools needed to develop high-performance, power-efficient robotics applications.
NVIDIA is also pioneering accelerated computing into ROS 2, and continuing to deliver improvements with each release. More than 20 hardware-accelerated ROS packages have been added in the past two years, with support for the latest ROS 2 distribution.
The company's team worked with Open Robotics last year to include adaptation and type negotiation to improve the ROS performance on compute platforms that offer hardware accelerators. They also implemented adaptation and type negotiation for Isaac ROS called NITROS (NVIDIA Isaac Transport for ROS).
The latest NVIDIA Isaac ROS Developer Preview 3 (DP3) release offers major updates and enhancements.
Understanding NVIDIA Isaac ROS Developer Preview 3
NVIDIA Isaac ROS DP3 includes many new features, enabling the ROS community to benefit from hardware acceleration. Highlights include a new map localizer to automatically localize the robot, updated NvBlox with human detection, the new ROS 2 benchmarking tool to realistically benchmark ROS 2 graphs, and open-source NITROS packages.
Automatically localize in a map in less than a half second
Mobile robots, such as those used in warehouses or service, need to know their initial pose in a map before starting to navigate the space. The most common method to provide this initial pose information to the robot is to manually set it. This method not only adds manual intervention to the whole process, but it can also take upwards of 30 seconds.
With the new Isaac ROS Map Location ROS package, there is no need to manually set the initial position and direction of the robot. This package uses lidar range scans to automatically estimate pose in an occupancy grid map in less than a half second.
The localizer can work with either planar or 3D lidar and can be used to initialize the navigation for mobile robots. This ROS package is GPU-accelerated and uses NITROS to create efficient ROS pipelines with no communication overhead. It is also integrated with Nav2.
For more information, see the Isaac ROS Map Localization package on GitHub.
Remove people from 3D reconstruction
Isaac ROS NvBlox provides a GPU-accelerated package for 3D reconstruction and a cost map of the environment around the robot using sensor observations. These are useful to path planners for generating collision-free paths.
Robots navigating among people need to first detect people and then navigate differently based on proximity to a person. Though people should be part of the cost map—to calculate a collision-free path to avoid people—they should not be part of 3D reconstruction. 3D reconstruction should include only static obstacles.
The updated Isaac ROS NvBlox package that is part of Isaac ROS DP3 release detects and segments people and provides a person cost map for avoiding collision with people. It also provides a static cost map for 3D reconstruction in order to avoid collision with static objects.
For more details, see the Isaac ROS NvBlox package on GitHub.
Benchmark ROS graphs the right way
Benchmarking ROS-based graphs should reflect the performance under a realistic workload. Benchmarking the entire ROS graph (instead of a particular ROS node) is important, as it will include the message transport costs in RCL indicative of real-world performance.
Isaac ROS DP3 includes benchmark tooling for ROS 2 in open-source. This tooling does not require modification of nodes to measure results, and standardizes input rosbag data sets for independent verification of benchmark results.
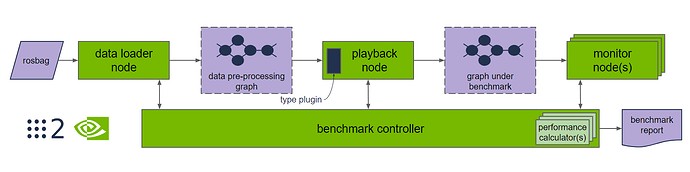
The benchmarking tool uses industry best practices and is professionally hardened for throughput and latency measurement of graphs of nodes in real-time robotics applications. Highlights include:
- Dependable results: Automated performance measurements are performed for multiple seconds N times (default N = 5), discarding minimum and maximum results to reduce variability. Benchmark results are reported in log files for import into your visualization tool of choice.
- Input data set: Available for download from NGC under CCv4 Attribution License, the r2b dataset 2023 provides a consistent input to the graph from rosbag. Users can add input datad when needed.
- Input image resolutions: With a broad range of computing hardware available, image processing is performed at different resolutions, depending on the robotics application.
- Input and output transport time: Time spent in RCL publishing and receiving messages for inter and intra process is included in the measurement results. This accurately represents what can be expected in a robotics application and avoids inflated results that remove message passing costs.
- Input and output type adaptation: Input data is injected using standard ROS types, or using type adaptation and type negotiation.
- Benchmark parameters: The parameters used for testing include data input length, publishing rate, and input size – and can be customized with a configuration file.
- Throughput auto finder: To measure peak throughput of the graph, with <1% topic drops, requires automatically finding the peak throughput of the graph. The throughout auto finder efficiently finds the input data publishing rate for peak throughput.
- Real-time latency: Fixed topic publisher rate for real-time measure of latency. This shows what is provided to the real-time system at the target fixed rate whereas throughput shows what peak performance is possible for the robotics application.
- Cloud-native: Measurements can be performed on Kubernetes as part of automated testing or CI/CD nightly testing as part of modern software development. Measurements can also be performed on local developer systems.
- Opaque testing: Graphs of nodes are tested as binaries with all performance measurement tooling in benchmark directly and does not modify code in the graph under test. This enables performance measurement inclusive of open source to proprietary solutions with the same tools in an unobtrusive way.
- Transparency: Results in JSON include the parameters used to run the benchmark, including an MD5 of the input rosbag for independent and verification of results.
Roboticists and developers can register for the webinar ”Performance Measurement of Robotics Applications with ros2_benchmark” to learn more.
Support for new platforms
Isaac ROS DP3 adds support for the newest members of the NVIDIA Jetson family, NVIDIA Jetson Orin Nano and NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX. It also supports the newly released NVIDIA Jetson Orin Nano Developer Kit. Isaac ROS is now supported on all Jetson Orin and Xavier series of modules and developer kits.
The new release also adds support for recently released NVIDIA Ada Lovelace architecture and NVIDIA GeForce RTX 40 GPUs.
Starting from this release, the majority of the NITROS accelerated Isaac ROS package is open-source. As an ROS developer, you can now extend the packages, fix any issues you encounter, and contribute back to the Isaac ROS community.
NVIDIA offers Isaac ROS developer resources
NVIDIA Isaac ROS Developer Preview 3 is a major update, enabling the ROS community to benefit from hardware acceleration to more easily build high-performance, power-efficient robotics applications. Highlights include the new ROS 2 benchmarking tool to realistically benchmark ROS 2 graphs, a new map localizer to automatically localize the robot, open-source NITROS packages, and updated NvBlox with human detection.
The company offers the following additional resources:
- Register for the webinar, Performance Measurement of Robotics Applications with ros2_benchmark.
- Read the Isaac ROS April update for more details and additional enhancements available in Isaac ROS DP3.
- Visit Isaac ROS on GitHub and get started with Isaac ROS DP3.
Engage with the community on the NVIDIA Isaac ROS Forum.

About the author
Suhas Hariharapura Sheshadri is a product manager at NVIDIA, focusing on Jetson software. He previously worked with the autonomous driving team at NVIDIA, optimizing system software for the NVIDIA Drive platform. In his free time, Sheshadri likes to read books on quantum physics and game theory.
Article topics
Email Sign Up

















