Editors’ Picks




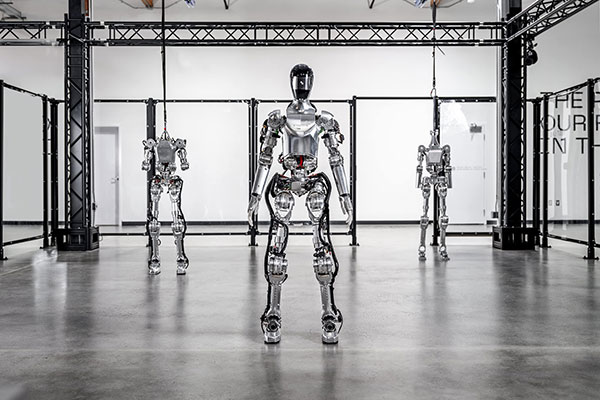
Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 48.15
…a $2.6B valuation. Series B investors came from Microsoft, OpenAI Startup Fund, NVIDIA, Jeff Bezos (through Bezos Expeditions), Parkway Venture Capital, Intel Capital, Align Ventures, and ARK Invest. Both Microsoft and OpenAI will collaborate with Figure to develop its robots. Figure said this investment will accelerate its timeline for commercial deployment of its humanoid robot. OpenAI collaboration aims to enhancing humanoid language processing In conjunction with its Series B investment, Figure and OpenAI have entered into a collaboration agreement to develop AI models for humanoid robots, combining OpenAI's research with Figure's robotics hardware and software. The collaboration aims to help…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 7.32
…and engaged lifestyle.” While robots such as ElliQ and OpenAI’s ChatGPT have shown promise in treating mental illness, some health professionals are still not convinced. At MIT, professor and psychologist Sherry Turkle said she worried that the interactions of machines “push us along a road where we’re encouraged to forget what makes people special.” “The performance of empathy is not empathy,” Turkle said. “The area of companion, lover therapist, best friend is really one of the few areas where people need people.” About the author Oliver Mitchell is a partner at ff Venture Capital. His areas of focus are drones,…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 8.32
…dexterity in recent years from the likes of both OpenAI and MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL). While the former is better known today for ChatGPT, in 2018, it made headlines by training a human-like robot hand to manipulate physical objects with unprecedented dexterity by using a reinforcement learning algorithm and code. CSAIL also relied on advances in deep learning to reorient a robotic hand to handle over 2,000 objects. As the pace of AI innovation continues to accelerate, we’re not far from seeing deep learning models for robotic dexterity deployed in real-world assembly lines. Giving robots awareness…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 29.42
…Fanuc, Kawasaki, Staubli, Yaskawa, Universal Robot, and more. Meanwhile, OpenAI's ChatGPT has blazed a trail for Large Language Models (LLMs), setting the AI world on fire. In Microsoft's paper “ChatGPT for Robotics: Design Principles and Model Abilities,” a key challenge in applying AI innovation to robotics is observed: “Robotics is a diverse field where several platforms, scenarios, and tools exist. There exists an extensive variety of libraries and APIs….” The paper proposed a higher-level function library and prompt engineering tools to control robots with natural language. LLMs have huge potential in robotics, a topic that READY Robotics co-founder and CIO,…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 26.42
OpenAI’s recently announced GPT-4 version of its ChatGPT text-generating artificial intelligence program is reportedly capable of “human-level performance” on many professional tests, beating 90% of human test-takers. According to the company, GPT-4 reached the 90th percentile on a simulated bar exam, the 93rd percentile on an SAT reading exam, and the 89th percentile on the SAT Math exam. Thanks to advances such as streamlining and large data sets, it produces fewer incorrect answers and is less likely to touch on taboo topics, said OpenAI. Despite some flaws and limitations, GPT-4’s capabilities are impressive, posing concerns about what else AI and…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 10.45
…expected it to be good at,” he noted. “As OpenAI opened up the API, I've played with it. It can pass a Turing Test, but it still makes mistakes. What's really exciting is using language models as a building block for other AI applications—not just generating text, but generating images or interacting with robots.” Schluntz's second prediction is that LLMs will enable engineers to build simple sets of instructions instead of needing to program every possible thing a robot might need to do. “The grounding problem in AI is that it has been good at classifying images of a dog…

Found in Robotics Companies & Businesses, with a score of 42.23
…understand, learn, or adapt, said the company, legally known as Emboided Intelligence Inc. Building on experience at Berkeley and OpenAI, the company's vision is the Covariant Brain: universal AI that allows robots to see, reason, and act on the world around them. It is bringing the Covariant Brain to commercial viability, starting with the industries that make, move, and store things in the physical world.
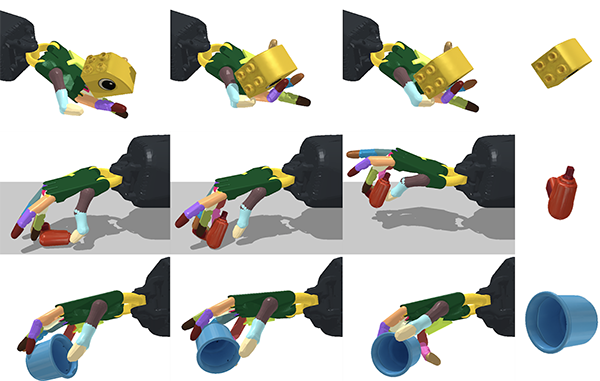
Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 10.97
…dexterous manipulation, according to the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. OpenAI gave it a try with “Dactyl” (meaning “finger” from the Greek word daktylos), using its humanoid robot hand to solve a Rubik’s cube with software that’s a step towards more general AI, and a step away from the common single-task mentality. DeepMind created “RGB-Stacking,” a vision-based system that challenges a robot to learn how to grab items and stack them. In the ongoing quest to get machines to replicate human abilities, scientists at the MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (MIT CSAIL) created a framework that’s more scaled up.…
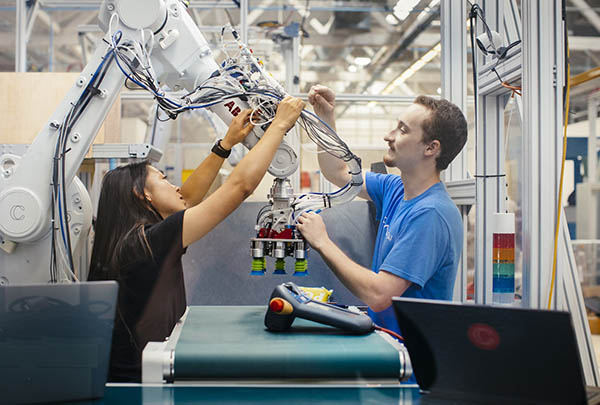

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 13.98
…and roboticists from the University of California, Berkeley, and OpenAI, Covariant said it is working to apply the latest AI breakthroughs to the biggest industrial opportunities. The company described its Covariant Brain as a “universal AI that allows robots to see, reason, and act on the world around them.” Covariant Brain deployments spread The Covariant Brain draws on its experiences across settings, verticals, and continents to allow customers from diverse industries to operate robots at human-level autonomy, said the company. In the past year, the Covariant Brain has been successfully deployed across industries including fashion, health and beauty, industrial supply,…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 37.56
…Role of AI in the World Microsoft Corp. and OpenAI, two companies thinking deeply about the role of AI in the world and how to build secure, trustworthy and ethical AI to serve the public, have partnered to further extend Microsoft Azure’s capabilities in large-scale AI systems. OpenAI was founded in late 2015 by Elon Musk and Sam Altman who were motivated in part by concerns about existential risk from artificial general intelligence. Through this new partnership, the companies will accelerate breakthroughs in AI and power OpenAI’s efforts to create artificial general intelligence (AGI). The resulting enhancements to the Azure…

Found in Robotics News & Content, with a score of 25.39
…months ago, Abbeel was a researcher at Elon Musk’s OpenAI lab. More recently, he co-founded Embodied Intelligence with three researchers from OpenAI and Berkeley. The company teaches robots how to pick parts and build assemblies using virtual reality and artificial intelligence. Modern: There are plenty of tech startups out there, but it isn’t every day that The New York Times writes a story about one of them less than a month after launch. Can you get us up to speed on what you’re doing? Abbeel: We’re trying to take robots to the next level in terms of their capabilities. It’s…



